CISFA uses Open Source Geographic Information Systems (e.g. QGIS) for weather, climate and environmental monitoring.
The G.I.S. or Geographic Information System is a tool that allows you to analyse, represent, query entities or events that happen in a specific territory. In the technology present within these software, they integrate with the common operations that can be carried out on spatial databases, such as searches, geometric and mathematical processing, statistical analyses, graphs. The functions of a G.I.S. such as the georeferencing of territorial data, their treatment and above all their representation in the form of cartograms or tables cut out on more or less large portions of territory, through their stylization and correlation in cartography.
These capabilities distinguish geographic systems from any other computing system by allowing users to have a tool that allows them to visualize and analyze information to explain events, plan, or design space infrastructure.
For all problems that have a geographical component, G.I.S allows you to create maps, integrate information, visualize even three-dimensional scenarios, solve complicated mobility problems and develop the most effective solutions.
For example, you will be able to locate any object on the ground or you will be able to study the evolution of the agricultural landscape or even study the paths of rivers over time.
Operations that are complicated if not impossible to carry out in the absence of this tool.
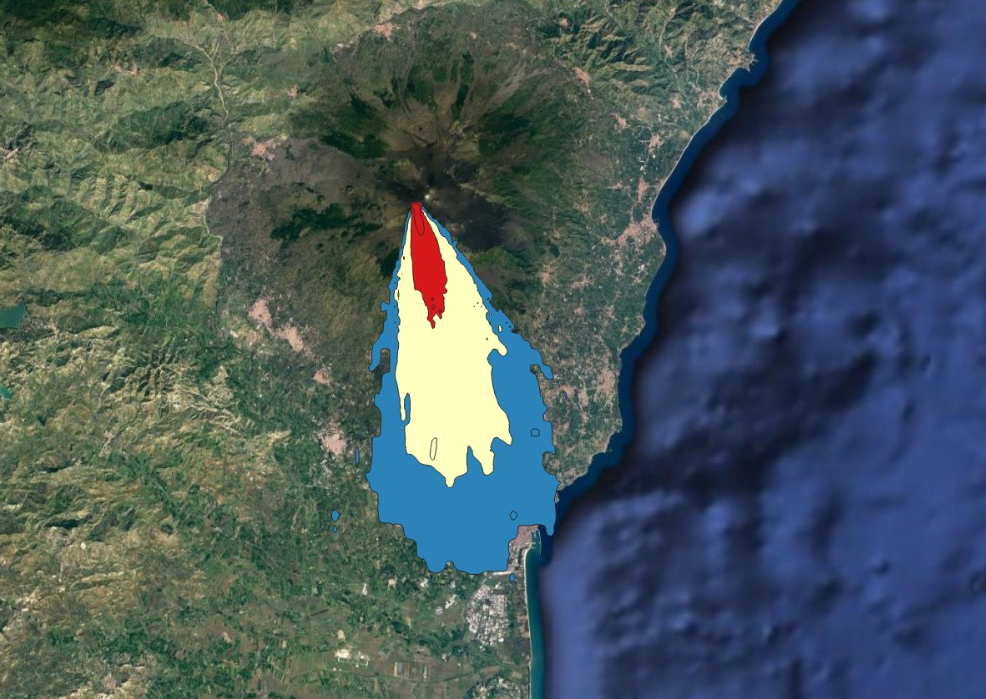
In particular, it makes use of these systems for the evaluation and correlation with the different meteorological models of the eruptions of the Sicilian volcanoes (Etna and Stromboli) of the dispersion and deposition of particles in the areas, with particular impact on air traffic. In the figure, specifically, an elaboration of the eruptions of the third week of February 2021 was made. The different colors depict the different post-eruption particle distribution in the different areas of the province of Catania and surrounding areas. The model was developed with the GDAS (Global Data Assimilation System) system, and subsequently georeferenced and stylized on QGIS.